(₹ crore)
| Product Segments |
Outstanding | Yo Y Growth % |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| FY2024 | FY2025 | ||
| Direct Credit | 26,826 | 37,781 | 41% |
| Refinance to Banks | 3,63,101 | 3,85,327 | 6% |
| Refinance to NBFC | 55,205 | 64,189 | 16% |
| Refinance to MFI | 8,771 | 6,054 | -31% |
| Cluster Development Fund Scheme |
2,111 | 2,931 | 39% |
| Total | 4,56,015 | 4,96,282 | 9% |
Institutional Finance accounts for approximately 92% of loans & advances of the bank. Outstanding under Institutional Finance was at ₹4,55,570 crore at the end of FY2025.
The Bank extends refinance assistance to augment resources of Primary Lending Institutions (PLIs) to increase flow of credit to MSMEs. The Refinance to Banks’ outstanding portfolio was ₹3,85,327 crore as on March 31, 2025, compared to ₹3,63,101 crore in FY2024 registering a Y-o-Y growth of 6.1%.
The refinance portfolio was spread across 50 PLIs, comprising 11 PSBs, 16 PVBs, 6 FBs, 8 SFBs, 7 RRBs and 2 UCBs and number of MSE customers under refinance was around 29.83 lakh.
During the year, disbursements under Refinance to Banks was effected in 40 PLIs benefitting 8.13 lakh MSE customers spread over all the 8 UTs & 28 States and 715 districts (out of 785 districts) in the country. 4 new PLIs were added to the portfolio during the year.
The cumulative disbursement out of MSE Refinance (MRF) since its inception in FY2009 up to FY2025 stood at ₹3,90,217 crore.
The NBFC portfolio outstanding of SIDBI as at the end of FY2025 stood at ₹64,189 crore compared to ₹55,205 crore during the previous year, recording an annual growth of 16%. The disbursements during FY2025 benefitted around 4.21 lakh MSME customers. The portfolio was spread across the entire spectrum of NBFCs from AAA to unrated NBFCs.
During the year, the Bank on-boarded 14 new NBFCs and at the end of FY2025, with total outreach under all schemes reaching 118 NBFCs. Further, the Bank extended financial assistance to 46 smaller NBFCs that were rated A and below/unrated.
The MFI portfolio outstanding of SIDBI as at the end of FY2025 stood at ₹6,054 crore compared to ₹8,771 crore during the previous year, recording decline of 31%.
During the year, microfinance sector witnessed increased indebtedness among end borrowers, decline in income, etc., resulting in recovery-related stress in MFI loan portfolios. Most of the NBFC-MFIs have made higher loan loss provisions and have written-off loans as a fallout of the stress in the sector.
There has been a decline in the offtake as MFIs laid more focus on their credit underwriting and recovery mechanisms. Given the strong headwinds, the Bank took a conscious call to slow down its intervention in the sector in line with the overall slowdown and strategically brought down the loan portfolio under the segment to align with the sectoral trend.
The Direct Lending portfolio through Branch Network, Partner Institutions and Digital Lending has grown by 41% during FY2025 with outstanding as at end of FY2025 at ₹37,781 crore as compared to ₹26,826 crore as at end of FY2024. The robust growth is primarily due to various structural and product-level interventions, viz., digitisation of entire lending process, introduction of new products, competitive rates, opening of new branches etc.
SIDBI extends direct credit through its branch network to MSMEs. Some of the key initiatives under Direct Lending-Branch Network during FY2025 were:
PARTNERSHIPS & COLLABORATIONS
For expanding customer outreach and designing innovative products, the Bank has been entering into partnership with various stakeholders with an objective of reaching out to new segments in MSMEs with focus on customer acquisitions. During the year, Bank entered into MoU with Axis Bank for extending Bank Guarantee to beneficiaries of MSME Customers of SIDBI where state government/beneficiaries do not accept BG issued by SIDBI. The Bank also entered into MoU with Receivables Exchange of India Limited (RXIL) to facilitate lending to the MSMEs registered on RXIL Platform for execution of work orders / acquiring machinery for capex purpose. Apart from the above, the Bank also entered into MoUs with Industry Associations, OEMs etc., to further lending to the MSME sector.
NEW/REVAMPED PRODUCTS
The Bank rolled out new products/product variants which mainly focus on catering to the emergent demands of MSMEs in their revival/growth trajectory. Existing Products such as EXPRESS, SWIFT, SWIFT-FT were revamped/modified keeping in view the market requirements.
To further expand the scope of “Straight through processing (STP)” to cover new to SIDBI customers, the Bank launched a new product viz., “Expeditious Process to deliver Rapid Loan through automated evaluation and Swift Sanction (EXPRESS 2.0)” to cater to the machinery/equipment finance requirements of MSMEs. The product framework envisages automated evaluation based on Financial Income & Trade (FIT) /CIBIL MSME Rank (CMR)/ JOCATA composite index of the entity and CIBIL credit vision score of promoters.
OPENING OF NEW BRANCH AND REGIONAL OFFICES
Pursuant to the announcement by the Hon’ble Finance Minister in the Budget speech, SIDBI has opened 26 New branches during FY 2024-25, taking the total of number of branches of SIDBI to 127 during FY2025, serving 176 MSME clusters in aggregate. The new branches will ensure better direct credit access to MSMEs located in the underserved regions and will also focus on micro loans, collateral-free business loans, machinery loans, etc.
To enhance outreach among MSMEs with focus on Informal Micro Enterprises (IMEs), SIDBI partnered with various financial intermediaries for extending direct credit leveraging the expertise and large network of channel partners viz., NBFCs, MFIs, Fintechs, BCs, etc.
With the above initiatives the direct lending through partner institutions portfolio nearly doubled with outstanding at the end of FY2025 at ₹5,760 crore, registering YoY growth of 98%.
Apart from the digital products such as EXPRESS that is extended through the branch network, the Bank scaled up financing under GST Sahay and TReDS.
The digital lending portfolio i.e., GST Sahay and TReDS registered a year-on-year growth of 52% with outstanding as at end of FY2025 at ₹2,170 crore.

SIDBI is involved in green finance initiatives to assist MSMEs in implementing sustainable practices. The institution has established a framework for advancing green financing within the MSME sector. Over time, SIDBI has gained experience and gathered insights through work with MSMEs related to sustainability efforts.
This is being implemented through two key schemes: the Green Finance Scheme (GFS) and the End-to-End Energy Efficiency Finance Scheme (4E). These two green credit products target the financial needs of energy efficiency, renewable energy, clean transport, circular economy/ waste management and adaptation projects. While the GFS caters to the financing needs of green project loans, the 4E scheme promotes investment in energy efficiency and renewable energy requirements for the brownfield/ existing enterprises. The green finance portfolio stood at ₹12,293 crore as at end of FY2025 contributing around 41% of the branch lending portfolio.
Energy savings
Reduction of GHG emission
MSMEs assisted
Sanctioned
Outstanding
Energy Efficiency investment – 75%
Renewable Energy (Solar & Wind) portfolio – 24%
Electric mobility & Circular economy sectors – 1%


SIDBI is the implementing agency for MSE Green Investment and Financing for Transformation (MSE GIFT) and MSE Scheme for Promotion and Investment in Circular Economy (MSE-SPICE) of MoMSME. The schemes encourage sustainable, eco-friendly practices and renewable energy use in Micro and Small Enterprises (MSEs) by offering interest subventions or subsidies, for investing in green technologies. During the FY2025, out of the total green loan extended, 1958 green loans have been covered under MSE-GIFT Scheme of Ministry of MSME (being implemented by SIDBI) for providing Interest Subvention (IS), out of which 560+ MSMEs have since availed the Interest Subvention.
SIDBI has operationalized thematic Risk Sharing Facility (RSF) on Energy Efficiency, Municipal Solid Waste and Electrical Vehicles. It is enhancing bankability and improved flow of credit to innovative/ emerging sectors / segments.
a) Partial Risk Sharing Facility for Energy Efficiency (PRSF) - PRSF implemented by SIDBI (supported by World Bank) is being replicated in multiple countries and has been picked as one of the 12 global models by OECD during COP 28. As on date, PRSF has been able to catalyse ESCO market with the investment of approx. USD 138 Mn with loan amount guaranteed to 83 projects of worth USD 84 Mn, leading to energy saving of 385 GWh/ yr. and emission reduction of 0.30Mn tCO2/ p.a.
b) EV-RSF (- SIDBI is running a Risk Sharing Facility for Electric vehicles, supported by Shell Foundation. The risk-sharing facility in the form of a second loss facility is being used to cover the EV loans sanctioned by financial institutions. It is estimated that around 8762 tCO2 are saved, per annum, with the 1904 EVs supported under EV-RSF, with a portfolio size of ₹68.21 crores covering 10 guarantees issued under the facility.
c) MSW-RSF - Under Risk Sharing Facility for Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) supported by GiZ, a total of 7 guarantees have been issued till date, supporting total projects of ₹147.73 crores and a portfolio coverage of ₹36.39 crores.
SIDBI is one of the Accredited Entity (AE) and Direct Access Entity of Green Climate Fund (GCF) and has positioned itself as one of the most suited DFI to channelize the climate funds directly for its project or anchoring the programs in the role of AE. Avaana Sustainability Fund (ASF) is a USD 120 Mn venture capital fund that aims to invest in early-stage climate technology companies in India. SIDBI has been instrumental in getting financial support of USD 24.5 million from Green Climate Fund (GCF) for the ASF program. In addition, GCF has sanctioned a loan of USD 200 Mn which will be blended with co-finance from SIDBI of up to USD 800 Million to finance the MSMEs for their green interventions. SIDBI has also availed green line of credit (LoC) from KFW (USD 150 Mn) and AFD (USD 100 Mn) for scaling up Green investment in MSME Sector and is continuously partnering with bilateral / multilaterals to scale up green investment in MSME sector.
SIDBI is developing smart clusters through EE Intervention. The initiative, called GRiT (Green Inclusivity), works through ESCO route where ESCOs are deployed to conduct workshops on energy efficiency and detailed energy audits in MSMEs.
This leads the MSMEs to fine tune their operations and invest in energy efficient technology, which is supported by Bank finance.
Start-up Venture Debt Scheme: The framework for venture debt to MSMEs/Startups launched by the Bank in FY2023 was scaled up significantly during FY2024 and FY2025. During FY2025, disbursements of ₹298 crore was undertaken with outstanding growing 2X to ₹402 crore as at end of FY2025.
Supporting India of tomorrow - Seed Fund through incubators: The Bank’s unique model for seed funding of impactful and product/IP-driven startups, in partnership with incubation centres resulted in increased coverage under the sanctioned seed fund corpus of ₹121 crore to across 16 incubators. The corresponding sanction to startups, increased from 1 with sanction of ₹2 crore in FY2023, to 71 startups with sanction of ₹41.58 crore in FY2025. This also included sanctioning an additional ₹13 crore to 3 incubators for defence sector startups during FY2025, taking cumulative sanction under defence sector to ₹38 crore to 8 incubators.

Under Fund of Funds, SIDBI contributes to SEBI-registered Venture Funds/AIFs, which must invest a specified portion of their corpus in MSMEs/startups per the scheme’s mandate.
Odisha Startup Growth Fund:
The fund was operationalised during FY2024 and as against present allocation/corpus of ₹100 crore, SIDBI has already committed ₹100 crore to 5 AIFs, ensuring full deployment of the available allocation.
Bihar Startup Scale-up Financing Fund:
Operationalised in FY2024, the fund has a present corpus of ₹50 crore. Out of this, SIDBI has committed ₹17 crore to 4 AIFs to support startup investments in the state.
Fund of Funds For Maharashtra:
With corpus of ₹100 crore, the fund of funds was operationalised in FY2025 for Maharashtra -based startups.
Uttar Pradesh Startup Fund:
The Government of Uttar Pradesh launched a startup fund worth ₹1,000 crore, managed by SIDBI. Last FY, the government released an additional ₹100 crore for facilitating contribution to various AIFs encouraging them to invest in startups, taking the total amount of fund released to ₹325 crore. During FY2025, ₹250 crore was committed under the scheme.
Above Maps are not to scale. For Illustrative purpose only.
The Government of India launched IMEF to provide equity support to smaller microfinance institutions (MFIs) to promote economic empowerment and financial inclusion. The Bank actively engaged with self-regulatory organisations and conducted outreach events in Ahmedabad and Kolkata, targeting MFIs in Western, Central, Eastern and North-Eastern regions. Consequently, ₹15 crore was sanctioned to 12 MFIs in FY2025.
The Bank has established a thorough Risk Management System that covers various areas such as Credit Risk Management, Market Risk Management, Operational Risk Management, Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process, Information Security Risk and Business Continuity Management.
The Bank’s Risk Management Committee monitors and manages the risks involved in its activities.
The Bank has following Risk Management Policies in place for various associated risks and its mitigation – Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Policy, Security & Collateral Management Policy, Market Risk Management Policy (MRMP), Operational Risk Management (ORM) Policy, IT Security Policy, Cyber Security Policy, Business Continuity Management (BCM) Policy, Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (ICAAP) Policy, Country Risk Management Policy, Assets Liability Management (ALM) Policy, Liquidity Management Policy, Investment Policy, Internal Control Guidelines for Derivatives (ICGD), Model Validation Policy and Basel-III Disclosure Policy.
The Policies of the Bank have been reviewed and updated as per RBI Master Directions on BASEL III which has also been approved by the Board. Necessary systems for CRAR Computation have been put in place and disclosures under Pillar 3 under BASEL III have been made. The Bank has implemented Basel III guidelines w.e.f. April 1, 2024.
The Bank has successfully integrated a new digital tool aimed at enhancing the loan underwriting process and credit rating mechanism. It is achieved through subscription-based services, which covers two key components viz:
The EWS mechanism in the Bank has been revamped and strengthened in line with RBI Master Directions dated July 15, 2024 ensuring better regulatory compliance and effective risk management system.
The Bank introduced quarterly Contingency Funding Plan and stress testing with monthly review along with introduction of review of liquidity on weekly basis for meeting liabilities during the week.

SIDBI has been laying emphasis on maintaining quality of portfolio and recovery from NPA accounts. A Board-level ‘Recovery Review Committee’ (RRC) is constituted to review all individual NPA cases having principal outstanding of ₹5 crore and above and SMAs, restructured accounts on quarterly basis. In addition, Board reviews the status of all NPAs, recoveries against NPAs, fresh slippages, details of reliefs granted, compromise settlements and prudential/actual write offs, on quarterly basis.
Recovery of ₹286 crore was made during FY2025, while Gross NPA of the Bank at the end of FY2025 stood at ₹183 crore (as against ₹100 crore in FY2024), Net NPA was Nil (as against Nil in FY2024).
SIDBI aims to reduce information asymmetry and support policymakers through knowledge products published with Credit Bureaus, etc., in multiple Indian languages.
The report provides insights into the Indian MSME sector based on a survey of 2,097 MSMEs across 19 sectors in manufacturing, services, and trading. It covers key challenges such as access to finance, technology adoption, competition, compliance, market access, infrastructure, supply chain, and skilled labour availability. The report also broadly estimates the credit gap for the MSME Sector in addition to providing valuable perspectives on the MSME sector.
An initiative by SIDBI-Transunion CIBIL, tracks credit health of MSMEs, offering insights to institutional lenders and stakeholders.
A SIDBI-Equifax quarterly report on credit trends in the Microfinance sector providing data-backed policy insights on the sector.
An MSME Economic Activity Index – Sumpoorn designed by SIDBI and Jocata. This MSME specific high frequency indicator captures the economic activity of India's growth engine with regards to MSMEs.
SIDBI - D&B designed an Index to provide a comprehensive overview of the sustainability landscape in the Indian MSME sector by assessing the internal and external factors that shape sustainability perception of businesses on three dimensions, namely –Awareness, Willingness, and Implementation of sustainability measures.
A quarterly pan-India survey of about 1,200 MSMEs on parameters ranging from business performance to availability of skilled labour, employment generation, capacity addition, financial access, cost of funds, ease of doing business, etc., to capture the MSMEs’ assessment of current business situation and the future expectations. The survey aims to address the critical data gap in the sector by producing MSME Business Confidence Index (M-BCI) and MSME Business Expectations Index (M-BEI).
Technology is being used by SIDBI to support the MSME sector. The Bank has been digitalising its decision-making and lending processes as well as implementing digital interventions in the ecosystem. Some of the important digital projects undertaken by the Bank are:
SIDBI, with support from DFS, has developed and maintained the Standup India and Udyamimitra portals under the Standup India program since 2016. Over 460 banks, NBFCs, and MFIs, connecting over 1.8 lakh branches, are registered on the portal. The Udyamimitra portal was revamped to enable SIDBI’s digital implementation of various credit/MSME schemes under different ministries, with customised workflows for multiple stakeholders. This plug-and-play model reduced onboarding time and enhanced program efficiency.
Some of the Flagship and impactful onboarded schemes using the UdyamiMitra Portal and Architecture are PMSVANidhi, PM Vishwakarma, Stand Up India, National Livestock Mission, Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund etc. SIDBI also created separate portals for different government programs, allowing for customised branding and easy integration with Udyamimitra, making it a valuable digital asset for SIDBI.

| Name of Program | Name of Ministry | Program Portal |
|---|---|---|
| Stand Up India | Department of Financial Services - Ministry of Finance | https://portal.standupmitra.in/ |
| National Livestock Mission | Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying - Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying | https://nlm.udyamimitra.in/ |
| Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund | Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying - Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying | https://ahidf.udyamimitra.in/ |
| Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Pharma | Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers | https://pli-pharma.udyamimitra.in/ |
| Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Telecommunications | Department of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications | https://pli-telecom.udyamimitra.in/ |
| PM SVANidhi | Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs | https://pmsvanidhi.mohua.gov.in |
| PM Vishwakarma | Ministry of Micro Small & Medium Enterprises | https://pmvishwakarma.gov.in/ |
| Strengthening of Pharmaceutical Industry | Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers | https://spi.udyamimitra.in/ |
| Assistance to Medical Device Clusters for Common Facilities | Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers | https://amdcf.udyamimitra.in/ |
| Vendor Connect Portal | Department of Telecommunications, Ministry of Communications | https://vendorconnect.udyamimitra.in/ |
| Swavalamban Challenge Fund | Small Industries Development Bank of India | https://scf.udyamimitra.in/ |
| Swavalamban Connect Kendra | Small Industries Development Bank of India | https://sck.udyamimitra.in/ |
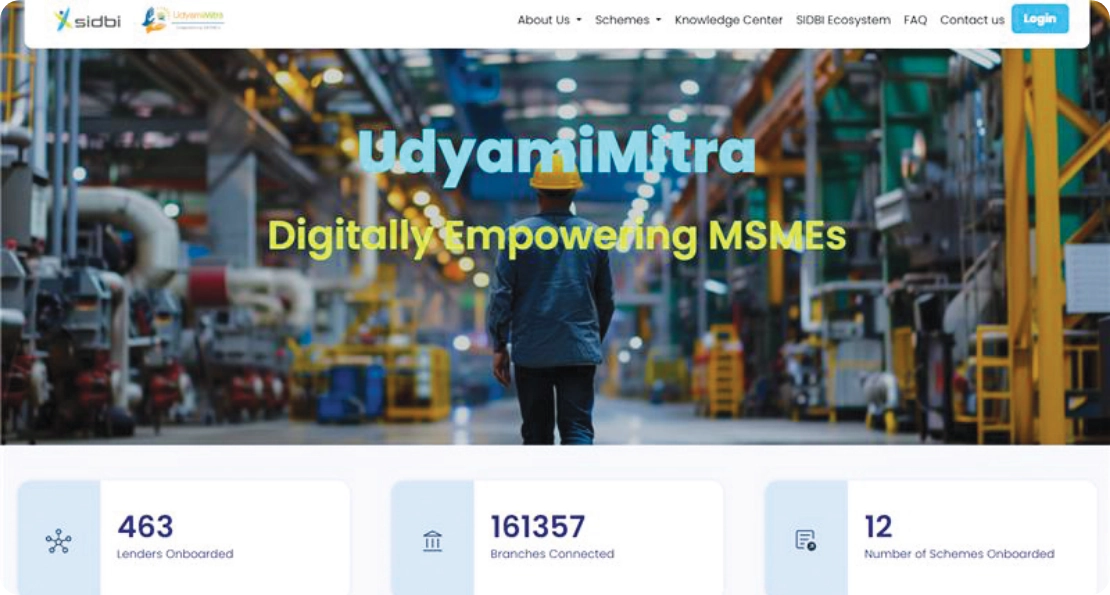
SIDBI also plays a key role in managing the various government schemes of the Government of India. Some of the major programs are listed below:

The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), Government of India, has been implementing the Prime Minister Street Vendor's AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) since June 1, 2020, to provide microcredit to urban street vendors impacted by COVID-19.

Ministry of Micro Small & Medium Enterprises (MoMSME) implements PM Vishwakarma scheme which aims to enhance the quality and reach of products and services by artisans and craftspeople.

SIDBI manages PLI Schemes for Pharmaceuticals (₹15,000 crore) and Telecom (₹12,195 crore).

Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers is nodal agency for the scheme. The SPI Scheme (₹500 crore till FY 2025-26) supports productivity in pharma clusters and MSMEs.

SIDBI is the implementing partner for National Livestock Mission (NLM) Scheme and Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) Scheme being implemented by Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD). SIDBI also plays the role of fund channelising agency for NLM Scheme.

SIDBI is the Project Management Agency (PMA) of the scheme being implemented by Department of Pharmaceuticals (DoP), Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers.

SCLCSS offers a 25% capital subsidy for SC/ST MSEs upgrading technology. Since the launch of the Scheme, capital subsidy claims aggregating ₹218.94 crore to 1,846 units have been released through SIDBI.
I. In line with its mandate of Development Financial Institutions (DFI), SIDBI plays a prominent role in promotion and development of MSMEs to address various non-financial challenges of MSMEs.
ii. The outcome of various activities of the Bank under Mission Swavalamban for the year are summarised as under:
Outreach: 3,05,500+
Persons Trained: 75,400+
Enterprise/Livelihood set up: 32,300+
Credit Connect: 18,870+
Market Connect: 8,140+

Intervention for Development of Industry Associations
The Bank has launched a program for development of Industry Associations in industrial clusters across India.
The program addresses challenges faced by Industry Associations through “soft” interventions like providing Business Support Executives for guidance and training, and “hard” interventions for office infrastructure development.
Micro Enterprise Promotion Programme (MEPP)
MEPP (erstwhile Rural Industries Programme – RIP) is an integrated programme for the creation of employment through microenterprises promotion. During FY2025, 1,149 units have been grounded, credit connect provided to 902 beneficiaries along with handholding support.
Swavalamban Challenge Fund (SCF)
SCF is a competitive digital mechanism to crowd-source innovative and outcome-driven solutions to development challenges. Since 2021, three SCF windows have been launched and received over 1,100 applications nationwide. In FY2025, over 7,000 beneficiaries have been mobilised and trained, 1,400+ enterprises/ livelihood have been generated, 340+ beneficiaries provided with formal credit and over 1,200 beneficiaries supported for market linkage.
Women Livelihood Generation Programme
SIDBI Supported Friends of Women’s World Banking, India for implementing the Women Livelihood Generation Programme (WLGP) involving the participation of 1,500 women from low-income households to create Livelihood/Nano/Micro-enterprises in 2 districts each in Assam, Meghalaya and Nagaland.
SWARAJ (Skilling Women and Youth with Indian Army in Jammu & Kashmir)
The project aims towards capacity building of 1,000 unemployed youths across 200 villages of the Rajouri and Poonch districts of J&K. Under the project, 750+ beneficiaries have been given skill training.
Establishing a Chair for Centre of Financial Inclusion at NI-MSME Campus, Hyderabad
SIDBI and CGTMSE set up a chair for Centre of Financial Inclusion (CFI) at the National Institute for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (NI-MSME) campus, Hyderabad with an objective to create awareness on financial literacy and credit counselling to MSEs, disseminate knowledge on financial prudence and develop formal & systematic credit avenues. In addition to the above, SIDBI has established chairs at Vivekananda Global University, Jaipur and Government Engineering College, Thrissur.
For other sections, download the - Annual Report Part I
Copyright © 2025 Small Industries Development Bank of India(SIDBI)
Designed and Developed by RDX Digital